Cost Audit
Cost audit is a systematic examination of a company's cost accounting records and activities to verify their accuracy, ensure compliance with legal standards, and identify opportunities for improvement. Here are the key details about cost audit:
It offers property damage coverage, personal property coverage, liability coverage, and temporary living expenses coverage. This coverage can help homeowners recover from significant financial losses due to unforeseen events. In addition, home insurance offers peace of mind to homeowners, knowing that their investment is protected against unexpected events that can be financially devastating.
Applicatbility:
Cost Audit is a legal compulsion for Companies according to COMPANIES (COST RECORDS AND AUDIT) RULES, 2014 [as amended upto 15th July 2016]
- Every company cited in item (A) of rule 3 whose yearly turnover during the immediately preceding FY is Rs 50 crores or more.
- Every company cited in item (A) of rule 3 whose total turnover of individual products or services for which cost records are mandated to be administered under rule 3 is Rs 25 crore or more.
- Every company cited in item (B) of rule 3 whose yearly turnover during the immediately preceding FY is Rs 100 crores or more.
- Every company cited in item (B) of rule 3 whose total turnover of individual products or services for which cost records are mandated to be administered under rule 3 is Rs 35 crore or more.
Purpose:
- Accuracy Verification: The primary aim is to ensure that the cost accounting records accurately reflect the company's operations, costs, and financial position.
- Compliance: It ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and standards set by regulatory authorities or governing bodies.
- Efficiency and Improvement: Identifies areas for cost reduction, operational improvements, and enhanced efficiency in resource utilization.
Scope:
- Cost Accounting Records: Examination of all cost accounting records, including ledgers, cost sheets, cost statements, and related documents.
- Process Evaluation: Assessment of cost accounting systems, methods, and internal controls.
- Compliance Check: Ensuring compliance with applicable laws, regulations, and accounting standards.
Conducting a Cost Audit:
- Appointment: An independent and qualified cost auditor is appointed by the company to conduct the audit.
- Data Collection: The auditor gathers data from various sources, including financial statements, cost records, invoices, and other relevant documents.
- Examination: Detailed examination and verification of cost records to ascertain their accuracy and compliance.
- Report Preparation: A comprehensive report is prepared by the auditor highlighting findings, compliance status, recommendations for improvement, and any discrepancies identified.
Legal Requirements:
- Cost audit may be mandatory for certain companies as per regulatory requirements in some jurisdictions, especially in industries where cost control and pricing regulations are critical (e.g., pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, etc.).
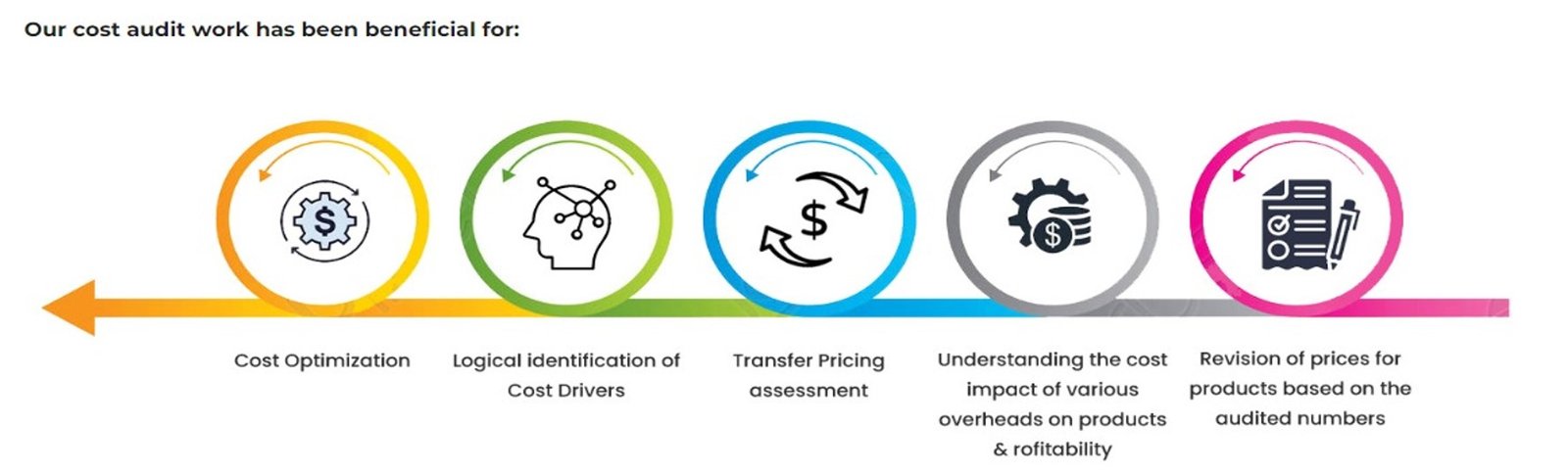
Benefits:
- Cost Control: Helps in identifying cost-saving opportunities and improving cost efficiency.
- Compliance: Ensures adherence to legal and regulatory standards.
- Operational Improvement: Every company cited in item (A) of rule 3 whose total turnover of individual products or services for which cost records are mandated to be administered under rule 3 is Rs 25 crore or more.
- Overall, cost audit plays a crucial role in ensuring financial accuracy, compliance, and identifying areas for improvement within an organization's cost accounting practices.
- Every company cited in item (A) of rule 3 whose total turnover of individual products or services for which cost records are mandated to be administered under rule 3 is Rs 25 crore or more.

